A system consists of several parts that are interconnected and interrelated, each part influencing each other through its dynamic nature while responding to the external influences as well. All the components within the system work to attain a common goal or purpose.
An influence in one part of the system will be felt throughout the system. It can be also referred to a spider’s web. Ludwig von Bertalanffy, a biologist has defined ‘General system theory’ as a set of elements that experience interrelationship among themselves and with their external environments.
A system is an assemblage or interrelated combination of things or elements or components forming a unitary whole (Hall 2008). Tourism can be referred to as a system as it reacts to the external environments like the social, political, technological and ecological. Elements like attraction, transport, accommodation, facilities interact with each other while it interacts with the external environment too.
Concept of Tourism as a System
Tourism is conceptualized as a system by many scholars. It was in the 1970s that the General Systems Theory was applied to the concept of tourism and it has resulted in a number of system theories of tourism. Scholars like Leiper, Getz, Gunn and Mill and Morrison have suggested systems model for tourism. In his book, tourism planning
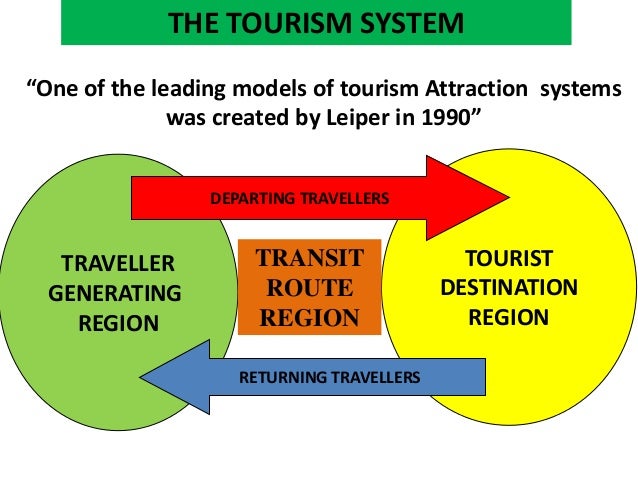
(1979), Gunn put forth the “tourism fundamental system” that involved five components: tourist, transportation, attractions, services-facilities, and information-direction. Leiper (1979) developed the whole tourism systems based on the systems theory and identified five basic components: tourists, generating regions, transit routes, destination regions, and a tourist industry operating within physical, cultural, social, economic, political, and technological environments. He conceptualized tourism as an open system.
Neil Leiper’s Whole Tourism System Model
Neil Leiper devised a Whole Tourism System Model in the year 1979 and the same was restructured in the year 1990. It is completely based on the Systems Approach consisting of three major components or elements. The following are the four components embedded in the Leiper’s model.
Pic credit- https://www.slideshare.net/Poddar25/got-3-module-1
I. The Human Component:
The Tourist
II. The Geographical Component:
• The Generating Region
• Transit Route Region
• The Destination Region
III. The Industrial Component
IV. The Environmental Component
Leiper proposed six aspects within the model which are interrelated, interdependent and interact with each other and function as a group while responding to the external influences. Thus it is an open system where influences are found within the system as well as external to the system.
The human component consists of the tourists, the geographical component consists of traveler-generating regions, transit route regions and tourist-destination regions, the industrial component involving the various business and organizations that provide services and finally, the environmental component comprising of the social, technological, legal and ecological aspects.
All these aspects weave together as a whole tourism system in a structural manner. Figure-1 provides the pictorial representation of the Leiper’s model of the components of the tourism system.
1. The Human Component
The human component specified in the model is the tourists who undertake tourism to a destination of their interests. A tourist is a person who traverses away from his place of residence to another place for a short span of stay with an aim to spend his holidays.
A person can be called as a tourist if he stays for at least 24 hours and not more than one year in a destination either within the country or outside the country of residence not involving in any remunerative activity. Tourism, according to the Oxford dictionary, is “the theory and practice of touring or travelling for pleasure”.
Tourists undertake different forms of tourism as per their need like recreation, pleasure, business, education, health, pilgrimage, culture and they are called as recreational tourists, pleasure tourists, business tourists, education tourists, health tourists, pilgrimage tourists and cultural tourists in that order.
It is based on the motivational push that tourists undertake their trip to a particular destination. It all happens with the available forms of tourism. Therefore, it completely depends on the purposes of travel.
As per the definition of UNWTO’s (United Nations World Tourism Organization), “tourism comprises the activities of persons travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes”. It is clear from the definition that tourists are temporary residents of the destination of visit.
After touring, they return to their original place of residence or their place of departure. According to Leiper (1979), the fundamentals of tourism are traced back to Greek origins, likened to a circle, reflecting a key component of tourism and returning to the point of departure.
2. The Geographic Component.
The geographic component refers to the geographical area involved in the tourism process. Tourists depart from a geographical area – the place of origin, utilize a geographical route and reach a geographical area – the place of arrival or destination of visit.
Similarly, they reach their area of origin after completion of the trip taking a complete cycle of the geographical components. Thus, there are three geographical areas involved in the conduct of tourism.
The geographic components comprise of the following three aspects:
1. Tourist Generating Region(TGR)
2. Travel Route Region(TRR) and
3. Tourist Destination Region(TDR)
2.1 Tourism Generating Regions (TGR).
Tourism Generating Region refers to the place where the tourist starts and ends his tour. It is the location of permanent residence from where he departs for tour and reaches after completion of trip. It is also referred to the source region of journey as well as the geographical area of demand. According to Dann (1977), it is the geographical setting pertaining to the motivational and behavioral pattern termed as “Push” factors.
‘Push’ factors are the intangible wishes or desires arising in the minds of a person. These are influenced by the social, psychological, and economic forces generated from within the person.
The aspects like mundane environment, exploration, self-evaluation, relaxation, prestige, family relations, and social interaction are found within the minds of the people of the tourist-generating region. These pertain to the psychological push factors. Influence of family, reference groups, social classes, culture, and sub-cultures are the factors pertaining to the social push factors.
The demographic aspects like age, sex, educational qualification, income and marital status also contribute to the push factors. The economic push factors are the disposable income added with the available leisure time joint together that play vital role in the tourist-generating region.
Apart from the above mentioned factors in the tourist generating region, the aspects like ticketing services, tour operators, travel agents and marketing and promotional activities present in the departure area play a major role as push components.
2.2. Transit Route Region (TRR).
Transit route refers to the path throughout the region across which the tourist travels to reach his or her destination. It is the path that links the tourist generating regions and the tourist destination regions, along which the tourists travel.
When the tourists undertake a long haul, travel it is necessary to take a temporary stoppage called a transit route. The transit route includes stopover points, which might be used for convenience of the tourist or due to the presence of various attractions throughout the travel route that can be visited by the tourists.
The transit route enables the tourists to change flight or stop for some time for refueling. The transit route might differ from the start of the travel from the generating region and ending of the travel from the destination region.
The transit route may be crossed with the different types of transportation like air transport or rail transport or water transport or road transport or a combination of all these types of transports according to the necessity of the tourist. Thus, the transit rout region is a vital component in the tourism system.
2.3 Tourist Destination Region (TDR).
Tourist Destination Region refers to the destination, which the tourists prefer to visit during their travel. It is the location, which attracts tourists for their temporary stay. The destination region is the core component of tourism, as it is the region, which the tourist chooses to visit, and which the core element of tourism is based on. It is the supply side of the tourism products that pull the tourists.
This component includes the natural attractions, cultural attraction, and various entertainment factors, accommodation, facilities, services, amenities, safety and security available in the destination of visit that ultimately pull the tourists. The new age tourists mostly demand now-a-days special interest tourism products available in the destination region.
The qualitative aspects that are absent or lacking in the tourist-generating region and available in the tourist destination region form as the basic attractions that pull the tourists towards TDR. The location has the attributes as anticipated by the tourists that retains loyal tourists from the generating regions
3. The Industrial Component..
The next important component in the Lieper’s model is the industry. Industrial component refers to the businesses and organizations that promote tourism related products. These firms thrive to cater to the needs and wants of the tourists.They impart full-fledged products and services to the tourists through attractions, accommodation, accessibility and amenities.
It is a composition of many small firms that provide tourist attractions and services to the tourists in an affordable manner. Tourism industry is not an individual entity and all the industrial components of the tourism industry function together as an amalgam as tourism cannot function in the absence of even a single aspect of the industrial component. Tourism industry is a mixture of many industries. They are:
• Tourist Services Industry
• Accommodation Industry
• Transport Industry
• Entertainment Industry
• Tourist Attraction Industry
• Shopping Industry
These industries are located in different places some in the tourist generating region and some in the destination region. The travel agents and tour operators are located in the tourist generating region who help in the arrangement of travel for the tourists.
They do marketing activities motivating the tourists to visit specific destination regions while designing tailor made tourism products. The travel agents and tour operators in the destination region are facilitators of the tourists. Thus, they form to be the tourist services industry.
The accommodation industry, the sub-component comprises of hotels, motels, resorts, guest- houses and home stays that provide temporary residential facility for the tourists. There is variety of options in the accommodation sector affordable to the different category of tourists. The transport industry consists of four forms of transport like air, rail, sea and road transport.
A number of carriers are there in the transport industry transporting the tourists from the tourist-generating region to the tourist destination region through the transit route region. It is one of the most indispensable components as tourism cannot happen without movement of people and transport industry solely takes care of it.
The entertainment industry pertains to the products provided in the destination region by the service providers with a motive to bring enjoyment, pleasure, fun, excitement, amusement and recreation to make the tourists’ leisure time fruitful and lively. Theaters, games, sports, gambling, bars and pubs are some of the products in the entertainment industry available in the destination region
The attraction industry comprises of the tourism experiences based on which tourists ultimately gets high level of satisfaction. Nature, culture, heritage, monuments, climate, beaches, events, sunshine, snow, are some of the attractions which pull the tourists towards the tourist destination region. Attractions are unique to the destinations, as these will not be found in the tourist-generating region.
Shopping Industry is another sub-component, which is unique to the destination region as tourists wish to shop products that are traditional or famous to that particular destination. For example, Kashmir is famous for shawls and Gujarat is famous for saris.
Therefore, tourists wish to buy souvenirs from the destinations and wherever they travel, they desire to go to some of the shopping malls to buy their choice products selected from souvenirs which happen to be ready-made wear, cosmetics / skin-care products, snacks / confectioneries, shoes/ other footwear, handbag /wallets/belts, souvenirs / handicrafts, medicine/ herbs, perfume, personal care and jewelry.

4. The Environmental Component.
The last component in the Leiper’s model of tourism system is the environment component that surrounds the three geographical regions. Tourism is an open system and it interacts with the external environment. Environment is the surrounding circumstances that affect the tourism system and vice versa. These forces either induce positive or negative influences on the tourism system. The environmental components that affect the tourism system are as follows:
1. Political Factors
2. Economic Factors
3. Social/Cultural Factors
4. Technological Factors
5. Environmental Factors
6. Legal Factors
4.1 Political Factors
Political factors influences the tourism system according the available political situation. An unstable political situation will hamstring the tourism development. Tourism system will function effectively if there is political harmony and law and order are executed in a proper manner.
It will further get developed in case the government enforces tourism policy planning, makes more investments in the tourism industry and ensures tax benefits. If there is good relationship existing between the countries of the tourist generating region and tourist destination region tourism will flourish. Otherwise tourism growth will be adversely affected.
4.2 Economic Factors
The economic factors influence the system of tourism as it is directly related to the per capita income of the tourist generating region, their disposable income and standard of living. On the other hand if tourist destination region provides affordable tourism products and services tourism development is likely to go up.
Therefore, the income and expenditure of the tourists will be balanced ensuring tourist flow. Economic factors are also directly related to the general global financial situation. The financial depression that was prevalent in the year 2008 had severely affected the tourism industry as the per capita income decreased all over the world.
4.3 Social/Cultural Factors
Social or cultural factors spell significant influences on the tourism system. Based on the attitude of the local people in the tourism destination region the tourists of the generating region will be pulled towards it. The experience of the tourists depends upon the receptive nature of the hosts of the destination.
If aversion prevails over the behavior of the tourists in the minds of the host people, loyal tourists cannot be pulled by the destination region. The tourists will not prefer to visit a destination which is not tourist friendly.
4.4 Technological Factors
Technology is another important factor that affects the tourism system. Technology has been developing swiftly and it has spread its wings in all the sectors especially in tourism. It has changed the travel behavior of the tourist of the generating region and the organizations of the tourism industry are using technology to market their their services and products of the tourist destination region.
Internet is used by the tourists to gather information about the destinations, the transit routes and the attractions to decide on their travel. They make reservations online instead of approaching the travel agents and tour operators – traditional methods of distribution system. The suppliers of the destination region and the transit route region like the airlines, hotels, and tourism attraction operators make direct contact with the tourists generating region and create great challenge to the intermediaries.
4.5 Environmental Factors
The environmental factors are related to the rich biodiversity existing in the tourist destination region. The more the pressure given to the environmental chasteness more will be the impact on the biodiversity. The ecosystem of the destination region is affected by the tourists of the generating region and the tourism industrial operators.
Negative impacts like pollution, loss of greeneries, congestion, over utilization creates the imperatives for making tourism sustainable for the future. Therefore, such negative impacts have to be eliminated or reduced by the government creating awareness about sustainability of tourism resources in the minds of the stakeholders otherwise severe loss will be exerted on the tourism system.
4.6 Legal Factors
The legal factors refer to the prevalent law and order in the tourist generating region, transit route region and the tourist destination region. These laws act as a framework to protect the tourists and the organizations of the tourism industry. It leads to the proper development and management of tourism and the components of the tourism system. There are laws pertaining to tourism infrastructure, conservation of natural rich biodiversity and the cultural resources.



